The Benefits of Fanless Computers

Understanding the Fanless Technology
Traditional computers rely on fans to stay cool, fanless computers achieve the same goal through passive cooling. Our fanless computers are designed without fans, relying on passive cooling to remain protected from environmental hazards. This ensures it can maintain long-term performance and durability even in the harshest environments.
Passive Cooling
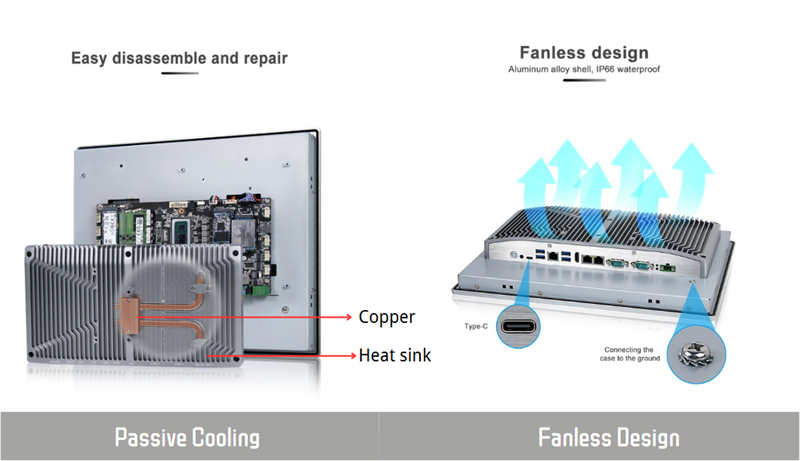
Passive cooling is a method of dissipating heat without using fans. This is the core of fanless computers. Fanless computers usually use a solid-state design and heatsinks to transfer heat away from the components. Heatsinks are the core component of this process, which plays a crucial role in transferring heat. Heatsinks usually use thermal paste or thermal pads to absorb the heat produced during operation and then transfer the heat to the extended aluminum housing.
Why Is Passive Cooling Important for Industrial Applications?
Rugged Computers use passive cooling techniques to remove detrimental heat away from critical components like the CPU. A key benefit from passive cooling is the elimination of moving fans and the use of exterior heatsinks to remove heat. Passive cooling designs increase the overall reliability and reduce common hardware failures associated with malfunctioning moving fans.
Fanless designs are popular among proven industrial and rugged applications that are exposed to dust, debris, and other harmful contaminants. Highly specialized conductive heat sinks made from aluminum and copper heat pipes effectively dissipate the heat away from critical components of the rugged computers. The ultra-durable enclosures are built with heatsink fins that effectively dissipate heat from the internal components to the surrounding natural air, creating a reliable passive cooling solution.
Although active cooling fans are easier to implement, they come with design shortcomings that are not suitable for industrial-grade deployments:
- 1. Ventilation Requirement
- 2. Noise Pollution
- 3. High Power Consumption
- 4. High Risk of Failure and Downtime
Benefits of Fanless Computers
1. Silent Operation
Fanless PCs achieve this silent operation through a combination of passive heat dissipation and solid-state drives (SSDs). Heat is drawn away from the CPU and GPU via onboard heat spreaders and extruded aluminum chassis that function as heatsinks. With no moving parts—including the use of SSDs instead of spinning disk drives—these systems operate in complete silence, reducing distractions and improving the user experience in environments where quiet is essential.

2. Dust, Debris, and Ingress Protection
This closed design enables many fanless industrial systems to meet ingress protection (IP) ratings such as IP5x for limited dust ingress or IP6x for fully dustproof construction. For applications that require waterproofing, ruggedized connectors and sealed I/O ports are used to meet IP65, IP66, or even IP67 standards. This makes fanless PCs a robust choice for harsh industrial or outdoor environments.
3. Shock and Vibration Resistance
- • Thicker PCBs to minimize board flex
- • Cableless architecture to prevent loose connections
- • Locking I/O connectors to ensure stable data and power delivery
These features allow fanless systems to meet rigorous testing standards such as MIL-STD-810G, withstanding up to 50G shock and 5GRMs of vibration—ideal for mobile or industrial deployments where reliability is critical.
4. High Reliability & Minimal Maintenance
The use of industrial-grade SSDs further enhances system resilience, offering faster data access and eliminating moving parts. Combined with rugged passive cooling and sealed chassis construction, fanless PCs are built for 24/7 operation in mission-critical environments, drastically lowering total cost of ownership (TCO) over time.
5. Compact & Space-Saving Design
This makes fanless mini PCs ideal for deployment in tight spaces such as electrical cabinets, control panels, vehicles, or mounted behind displays. Many models offer low-profile or DIN-rail mounting options to support diverse installation needs.
6. Wide Temperature Range and Environmental Endurance
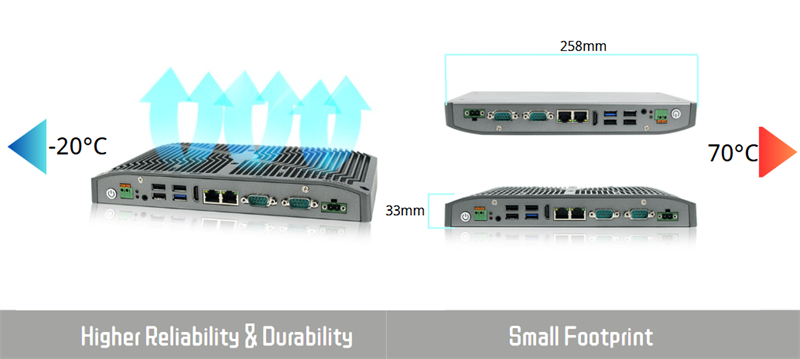
The chassis, often made of aluminum, acts as a large heatsink, efficiently dissipating heat away from internal components. Combined with shock and ingress protection, fanless PCs are well-suited for remote outdoor applications, transportation, oil and gas sites, and other demanding industrial use cases.
7. Lower Power Consumption
Lower power consumption results in reduced heat output and increased system stability, especially in thermally constrained environments. For large-scale IoT or edge deployments, the cumulative energy savings are substantial. Additionally, lower TDP (thermal design power) processors often still deliver competitive performance thanks to architectural improvements.
At InnoAioT, our fanless computers are designed with high reliability and durability. Removing the fans from computers not only prevents dust and debris but eliminate the heat to ensure the operation and high performance.
