Motherboard Form Factors Explained
When making or improving a computer, you must know about motherboard form factors. These form factors determine the shape, size, and layout of the board. They indicate where components like the CPU, RAM, and ports are placed. Choosing the right motherboard form factor ensures that your parts fit and function optimally.
Did you know that motherboard form factors also influence computer designs? Smaller boards create compact devices, while larger ones accommodate powerful systems.
Understanding motherboard form factors helps you select components that fit and perform best.
Key Takeaways
- • Motherboard form factors decide the size and shape of a motherboard. Picking the right one makes sure all parts fit and work well.
- • ATX motherboards are great for gaming and powerful tasks. They have more slots for upgrades and better cooling than smaller boards.
- • Mini-ITX boards are small and good for tiny builds like home theater PCs. But they don’t allow many upgrades because of their size.
- • Knowing the differences between motherboard types helps you choose the best one. This depends on if you need it for gaming, saving money, or small setups.
- • Industrial motherboards are made for tough places. They are strong and dependable, so they work well in factories, medical tools, and transport systems.
What is a Motherboard?
Definition and Role of a Motherboard
A motherboard is the main part of a computer. It connects all the parts so they can work together. Think of it as the system's backbone. It holds the CPU, RAM, storage, and other devices to make the computer work.
Here are some important parts of a motherboard:
- 1. CPU Slot: Holds the processor to run programs and do calculations.
- 2. RAM Slot: Stores temporary data for quick access while the computer runs.
- 3. Expansion Slot: Adds extra hardware like graphics or sound cards.
- 4. Northbridge and Southbridge: Help the CPU, memory, and devices communicate.
- 5. USB Ports: Connect external devices like keyboards, mice, and flash drives.
Motherboards have changed a lot over time. In the 1970s, computers had separate boards for the CPU and other parts. By the 1990s, they combined audio, video, and networking features into one board. Today, they are smaller and faster, supporting advanced features like high-speed USB and multiple GPUs.
Importance of Motherboard Form Factors in Computer Design
Motherboard form factors decide how a computer looks and works. They set the size, shape, and layout of the board. This affects how parts fit and work together. For example, ATX boards have more space for extra slots and cooling, great for gaming or editing. Smaller boards like Mini-ITX are good for compact setups like home theater PCs.
Form factors also affect performance. Bigger boards allow more RAM and GPUs, making upgrades easier. They also have space for cooling systems to prevent overheating. Picking the right form factor ensures your parts fit and work well.
| Feature | Effect on Performance |
| Compatibility | Makes sure parts fit and work together. |
| Expandability | More slots for RAM and GPUs improve options. |
| Cooling Capabilities | Space for cooling prevents overheating. |
Overview of Motherboard Form Factors
What Are Motherboard Form Factors?
Motherboard form factors set the size and shape of the board. They decide how parts like the CPU and RAM are placed. These details make sure the board fits in the case and works with other parts.
Over time, new form factors were made for different needs. For example, IBM's XT form factor came out in 1983. It was 216 × 279 mm (8.5 × 11 in) and used in early computers. But now, it is outdated. Modern types like ATX and ITX are faster and more flexible for today’s computers.
Why Are Motherboard Form Factors Important?
Motherboard form factors affect how a computer works and looks. They decide the computer’s size, parts it can hold, and cooling ability. Bigger boards like ATX can hold more CPUs and slots. This makes them great for gaming or work computers. Smaller boards like Mini-ITX are good for tiny setups like media centers.
Standards like HPM-FLW and HPM-DNO help with part compatibility. HPM-FLW fits server racks and supports two CPUs. HPM-DNO works for smaller servers, making them easier to use.
| Specification | Description |
| HPM-FLW | Fits 1U and 2U racks, supports two CPUs. |
| HPM-DNO | Made for smaller servers, faster to set up. |
Picking the right form factor helps your computer do what you need. Whether for gaming or a small media setup, the form factor decides what’s possible.
Common Motherboard Form Factors
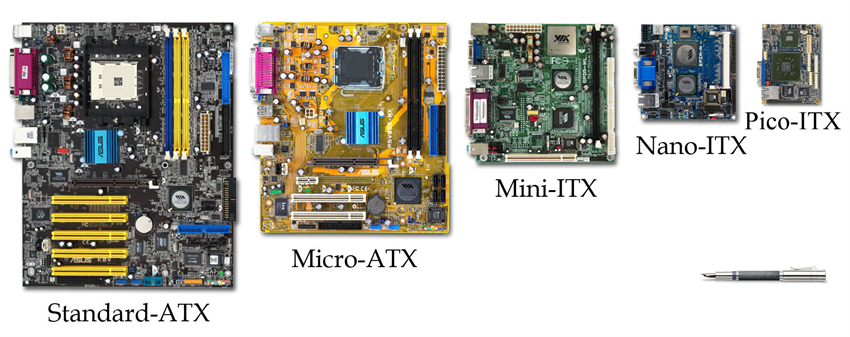
When picking a motherboard, you’ll see different sizes for various uses. Let’s look at three popular types: ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX.
ATX
ATX stands for Advanced Technology eXtended. It’s a favorite for desktop computers. ATX boards are 12 x 9.6 inches in size. They have space for seven expansion slots and up to four RAM slots. This makes them great for gaming, editing videos, or other demanding tasks.
Tip: Want a strong PC with multiple GPUs or advanced cooling? Choose an ATX motherboard.
Here’s how ATX compares to other sizes:
Form Factor
Dimensions
Expansion Slots
DIMM Slots
ATX
12” × 9.6”
7
4
Extended ATX
12” x 13”
More than 7
More than 4
Micro-ATX
9.6” × 9.6”
2
4
Mini-ITX
6.7” × 6.7”
1
2
ATX boards fit bigger cases, giving room for upgrades and airflow. They’re a flexible choice for most users.
Micro-ATX
Micro-ATX boards are smaller than ATX, measuring 9.6 x 9.6 inches. They still work well despite their size. You get up to four RAM slots and two expansion slots. These boards are good for budget builds or simple setups.
Micro-ATX is popular because it’s affordable and useful. It’s great for home office PCs or low-cost gaming systems.
Note: Micro-ATX boards are often used in small servers or compact desktops.
Why Micro-ATX is a good choice:
- • Small size fits tiny cases.
- • Low price is great for saving money.
- • Works for gaming, office tasks, and light server use.
Mini-ITX
Mini-ITX boards are the smallest, at 6.7 x 6.7 inches. They’re made for small builds like home theater PCs or compact gaming systems. Even though they’re tiny, they can handle strong processors and graphics cards.
Mini-ITX boards have limits. They usually have one PCIe slot and two RAM slots. This means fewer upgrade options. If you need a portable or sleek PC, Mini-ITX is a smart pick.
| Feature | Mini-ITX | Larger Form Factors (ATX, Micro-ATX) |
| Dimensions | 6.7 x 6.7 inches | Bigger sizes |
| Expansion Slots | Limited (1 PCIe slot) | More slots available |
| RAM Slots | Usually 2 | More slots available |
| Use Cases | SFF builds, HTPCs | Gaming, workstations, general use |
| Compatibility | Fits in larger cases | Needs specific case sizes |
Tip: Building a small PC? Mini-ITX is perfect. Just remember, upgrades are limited.
Each motherboard size has pros and cons. Knowing their features helps you pick the right one for your needs.
Nano-ITX
Nano-ITX boards are made for small systems with limited space. They measure 120mm x 120mm, smaller than Mini-ITX, but still support key parts. Their compact size works well for digital signs, portable gadgets, and embedded systems.
These boards are great when size and efficiency are important. They often have built-in processors and memory to save space. This design reduces extra parts, making systems lighter and more energy-efficient.
Key Features of Nano-ITX:
- • Compact Size: 120mm x 120mm fits in tight spaces.
- • Low Power Use: Great for energy-saving devices.
- • Built-In Parts: Many models include processors and memory.
Tip: Building for IoT or a small media player? Nano-ITX is a smart pick.
Pico-ITX
Pico-ITX boards are even smaller, at 100mm x 72mm. They handle basic tasks and are used in robots, industrial tools, and tiny devices. Their size makes them perfect for specialized uses.
These boards focus on efficiency, not upgrades. They often have fixed processors and fewer connection options. This makes them ideal for tasks that don’t need frequent changes.
Why Choose Pico-ITX?
- • Tiny Design: 100mm x 72mm fits the smallest spaces.
- • Strong Build: Made for tough environments.
- • Special Uses: Great for robots, automation, and portable tools.
Note: Pico-ITX isn’t for gaming or heavy tasks. Use it for simple, specific jobs.
FEMTO-ITX
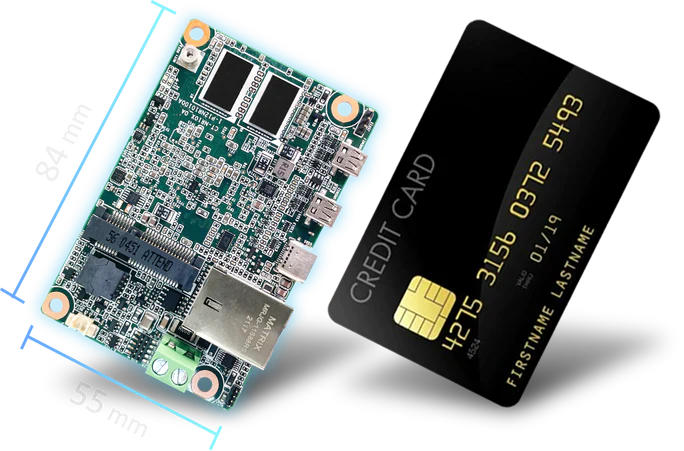
FEMTO-ITX is the tiniest motherboard, measuring 84mm x 55mm. It’s made for ultra-small systems where every bit of space matters. You’ll see these in wearables, medical tools, and unique devices.
Because they’re so small, FEMTO-ITX boards have few upgrade options. They usually come with built-in processors and limited ports. Their size allows for creative designs not possible with bigger boards.
Advantages of FEMTO-ITX:
- • Smallest Size: 84mm x 55mm for ultra-compact designs.
- • Specialized Use: Best for wearables and medical tools.
- • Energy Saving: Uses very little power, great for battery devices.
Tip: Working on a tiny, advanced project? FEMTO-ITX is the best choice.
Detailed Breakdown of Motherboard Form Factors
ATX
ATX stands for Advanced Technology eXtended. It is a popular motherboard size. Its standard size is 12 × 9.6 inches (305 × 244 mm). This size fits mid-tower and full-tower cases. ATX boards have space for seven expansion slots and four RAM slots. They support multiple GPUs, making them great for gaming and editing.
ATX boards are reliable and well-designed. Their layout allows good airflow, which prevents overheating. The larger size also supports strong power systems. This helps with overclocking and running high-performance CPUs. Below is a table comparing ATX with other sizes:
| Form Factor | Dimensions (inches) | Dimensions (mm) | Characteristics |
| E-ATX | 12 × 13 | 305 × 330 | More DRAM and expansion slots |
| ATX Standard | 12 × 9.6 | 305 × 244 | Original ATX form factor |
| microATX | 9.6 × 9.6 | 244 × 244 | Also known as μATX, uATX, and mATX |
| Mini-ATX | 5.9 × 5.9 | 150 × 150 | Also known as Mini ATX |
Tip: Choose ATX if you want a flexible board with upgrade options.
Micro-ATX
Micro-ATX, or mATX, is a smaller version of ATX. Its size is 9.6 × 9.6 inches (244 × 244 mm). It fits in smaller cases but still offers good expandability. Most Micro-ATX boards have up to four RAM slots and two to four expansion slots. This makes them a good choice for budget builds and compact PCs.
Micro-ATX keeps many features of ATX. It works with most modern CPUs and GPUs. However, its smaller size can limit airflow, causing higher temperatures. Using proper cooling is important for the best performance.
Micro-ATX is a great option for those who want a balance of size, cost, and features. It is affordable and works well for first-time PC builders.
Mini-ITX
Mini-ITX is the smallest form factor discussed here. Its size is 6.7 × 6.7 inches (170 × 170 mm). It is made for small builds like home theater PCs or portable gaming systems. Despite its size, Mini-ITX can handle powerful CPUs and GPUs.
However, Mini-ITX has some limits. It usually has one PCIe slot and up to two RAM slots. The small size also means fewer VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules), which affects overclocking. Tight spacing can also cause heat problems. The table below compares Mini-ITX with Micro-ATX:
| Feature | Mini-ITX | M-ATX |
| Dimensions | 6.7 × 6.7 inches | Larger than Mini-ITX |
| PCIe Lanes | Typically 1 | Multiple available |
| RAM Slots | Up to 2 | Up to 4 |
| VRMs | Fewer than larger boards | More VRMs available |
| Overclocking Capability | Limited due to fewer VRMs | Better support for overclocking |
| Heat Dissipation Issues | More potential due to compactness |
|
Note: Mini-ITX is great for small builds but needs careful planning for cooling and upgrades.
Each motherboard size has its own pros and cons. Knowing these differences helps you pick the right one for your needs.
Nano-ITX
Nano-ITX motherboards are small, measuring 4.7 × 4.7 inches. They are made for embedded systems like digital signs, kiosks, and IoT devices. Their compact size fits tight spaces while supporting key parts.
These boards often have built-in processors and memory. This saves space and reduces the need for extra hardware. They are lightweight and use less energy. Despite being small, they perform well for specific tasks.
| Form Factor | Dimensions | Applications | PCIe Slots |
| Nano-ITX | 4.7 × 4.7 in | Embedded System | 1x PCIe x16, 1x Mini-PCIe |
| Pico-ITX | 3.9 × 2.8 in | Embedded System | 2x Half-sized mini PCIe |
Pico-ITX
Pico-ITX motherboards are even smaller at 3.9 × 2.8 inches. They work well in tiny systems like robots, tools, and portable gadgets. Their small size makes them great for tight spaces.
These boards usually have two half-sized mini PCIe slots for basic upgrades. They focus on efficiency, not power, and are best for tasks needing little change. Below is a comparison of Pico-ITX with other small boards:
| Form Factor | Dimensions | Applications | PCIe Slots |
| Mini-ITX | 6.7 × 6.7 in | Small Form Factor | 1x PCIe x16, 1x Mini PCIe |
| Nano-ITX | 4.7 × 4.7 in | Embedded System | 1x PCIe x16, 1x Mini-PCIe |
| Pico-ITX | 3.9 × 2.8 in | Embedded System | 2x Half-sized mini PCIe |
Note: Pico-ITX isn’t for gaming or heavy tasks. It’s best for small, specific jobs.
FEMTO-ITX
FEMTO-ITX is the tiniest motherboard, measuring 3.3 × 2.1 inches. These boards are used in wearables, medical tools, and smart devices. Their small size allows creative designs not possible with bigger boards.
Even though they’re tiny, FEMTO-ITX boards have great features. They can run two 4K displays and offer expansion options like mPCIe slots. Their energy-efficient design supports powerful CPUs for advanced uses.
| Feature | Description |
| Form Factor | 1.8" FEMTO-ITX Single Board Computer |
| Size | 84mm x 55mm (3.31″ x 2.17″) |
| Power Management | Energy-efficient CPUs onboard for space-constrained environments |
| Connectivity | LAN, USB, M.2, or mPCIe expansion for enhanced capabilities |
- Key Advantages:
- • Tiny and lightweight design
- • Strong power for smart computing
- • Expansion through mPCIe slot
- • Supports two 4K displays
Tip: FEMTO-ITX is perfect for small, advanced projects like wearables or medical devices.
Comparison of Motherboard Form Factors
Summary Table of Dimensions, Uses, and Features
Knowing the size, uses, and features of motherboards helps you choose wisely. Each type fits different needs, like gaming or small builds. The table below shows key details:
| Form Factor | Dimensions (inches) | Uses | Features |
| ATX | 12 × 9.6 | Gaming, workstations | Many slots, good cooling |
| Micro-ATX | 9.6 × 9.6 | Budget PCs, compact builds | Cheaper, fewer slots |
| Mini-ITX | 6.7 × 6.7 | Small PCs | Tiny size, fewer upgrades |
| Nano-ITX | 4.7 × 4.7 | IoT, embedded systems | Built-in parts, saves energy |
| Pico-ITX | 3.9 × 2.8 | Robots, portable devices | Very small, special uses |
| FEMTO-ITX | 3.3 × 2.1 | Wearables, medical tools | Ultra-small, advanced features |
Tip: Use this table to match your needs. For gaming, pick ATX. For IoT, Nano-ITX is best.
Main Differences Between ATX and Smaller Boards
ATX boards are bigger than Mini-ITX or Nano-ITX. These differences affect how they work and what they’re used for. ATX boards have more slots and better cooling, great for gaming or heavy tasks. Smaller boards save space, perfect for tight setups.
Here’s a comparison of pros and cons for each type:
| Form Factor | Pros | Cons |
| Standard ATX | Fits smaller cases, works with ATX/EATX cases | Fewer slots, less airflow in small cases |
| Micro-ATX | Compact, affordable | Limited upgrades |
| eXtended ATX | Best for high-performance tasks | Needs big cases, costs more |
Mini-ITX boards trade expandability for size. They have fewer RAM slots and PCIe lanes, so upgrades are limited. ATX boards allow multiple GPUs and advanced cooling. If you want power, go with ATX. For small builds, Mini-ITX or Nano-ITX is better.
Note: Pick ATX for power and upgrades. Choose smaller boards to save space.
Industrial Motherboards
What Are Industrial Motherboards?
Industrial motherboards are special boards made for tough environments. Unlike regular motherboards, they focus on being strong, reliable, and lasting a long time. You’ll see them in places like factories, hospitals, and transportation systems.
These boards can handle harsh conditions like heat, dust, and shaking. They are built to last for years without needing frequent replacements. Their design ensures they work well with industrial parts, making them perfect for important tasks.
Did you know? The market for industrial motherboards is growing fast. By 2024, it’s expected to hit USD 2.0 billion and grow to USD 3.1 billion by 2033, with a steady growth rate of 4.73%. This shows the rising need for automation and smart factories.
Key Features of Industrial Motherboards
Industrial motherboards have special features that make them different from regular ones. These features help them meet the tough demands of industrial use.
| Component | Function | Design Considerations |
| Chipset | Controls data flow between CPU, memory, and devices. | Affects compatibility, slots, and heat control. |
| CPU Socket | Holds the CPU securely. | Matches specific CPUs and ensures proper cooling. |
| RAM Slots | Holds memory for fast data processing. | Supports high-speed memory like DDR5. |
| Expansion Slots | Adds extra parts like GPUs or network cards. | Fits different card sizes and supports fast data transfer. |
| Connectors | Links power, storage, and other devices. | Designed for easy access and strong signals. |
These boards also work in wide temperature ranges, have better power control, and support older ports. Their strong build makes them work where regular boards would fail.
Tip: When picking an industrial motherboard, think about what you need. Look at performance, size, and power limits to find the right one.
Applications of Industrial Motherboards
Industrial motherboards are used in many industries. Their strength and flexibility make them useful in different areas:
- • Manufacturing and Automation: Used in robots, factory machines, and assembly lines. They help with smart factories and automation trends.
- • Medical Equipment: Found in tools like scanners and diagnostic machines. They ensure accurate results in healthcare.
- • Transportation Systems: Used in trains, traffic systems, and vehicle checks. They handle vibrations and extreme weather well.
- • IoT and IIoT Devices: Important for smart gadgets and industrial IoT systems. They process data quickly and connect devices.
- • Energy and Utilities: Used in power grids, renewable energy, and utility systems. Their long life ensures smooth operation.
The growth of IoT and IIoT has increased the need for industrial motherboards. Their durability and reliability make them essential for modern industries.
Note: As automation and smart factories grow, choosing the right motherboard is crucial. Look for durable parts and advanced technology compatibility.
Knowing motherboard form factors helps you build the right computer. Each type has its own advantages. ATX boards have more slots and better cooling, perfect for gaming or heavy tasks. Micro-ATX is smaller and cheaper, great for budget-friendly builds. Mini-ITX is tiny and fits compact setups but has fewer upgrade options.
Tip: Pick a form factor based on your needs. For high performance, choose ATX. For small spaces, go with Mini-ITX. Always ensure the form factor matches your case and parts for the best fit.
Form Factor
Best Use
Main Features
ATX
Gaming, editing
More slots, better cooling
Micro-ATX
Budget builds
Small size, low cost
Mini-ITX
Compact setups
Saves space, portable
FAQ
What is the best motherboard form factor for gaming?
ATX is great for gaming. It has many expansion slots and supports strong GPUs. Its size allows upgrades and better cooling, perfect for gaming or editing.
Can I use a Mini-ITX motherboard for a powerful PC?
Yes, Mini-ITX can run strong CPUs and GPUs. But it has fewer slots and less RAM space. It’s best for small builds where space is more important than upgrades.
How do I choose the right motherboard form factor?
Think about your needs. For gaming or heavy tasks, pick ATX. Micro-ATX is good for saving money. Mini-ITX works for small setups. Make sure the board fits your case and has the features you need.
Are smaller motherboards less powerful?
Not always. Small boards like Mini-ITX can handle strong processors. But they have fewer upgrade slots and may get hotter because of their size.
Do industrial motherboards differ from regular ones?
Yes, industrial boards are tougher. They handle heat, dust, and shaking. They last longer and work well in factories, medical tools, and transport systems.
