Resistive Touchscreen vs Projected Capacitive
Time:2025-09-02 15:43:23
Visit:231
What is a Touchscreen?
A touchscreen is a display technology that allows users to interact with a computer by directly touching the screen, eliminating the need for a mouse. Touchscreens are widely used across different industries, including kiosks, digital signage, automation, transportation, and more.
When choosing the best touchscreen technology, two main options are available: Resistive and Projected Capacitive (PCAP). Both have their unique advantages and applications, with PCAP being preferred for consumer electronics due to its precision, while Resistive technology is commonly used in industrial environments for its robustness. This article compares both technologies to help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs, whether you're developing consumer products or setting up industrial systems.
What is a Capacitive (PCAP) Touchscreen and How Does it Function?
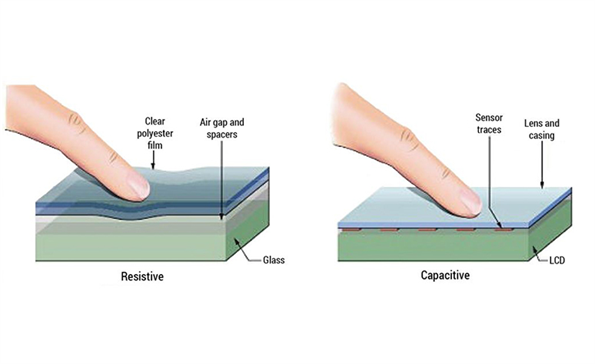
PCAP, or Projected Capacitive, is the standard capacitive touchscreen technology used in most modern applications. It consists of a protective glass layer, an electrode grid that generates an electromagnetic field to sense conductivity, and a glass substrate. When a conductive object, like a finger, touches the screen, it alters the electromagnetic field at the point of contact. This change is detected by a controller that identifies the location and processes the touch input.
PCAP Features
PCAP touchscreens are ideal for industrial applications, mainly due to their support for multiple touch points (multi-touch). This feature allows gestures such as pinch-to-zoom with two fingers. Additional benefits of PCAP include:
- • Excellent clarity and readability thanks to the transparent nature of the screen
- • Highly accurate touch functionality
- • Superior sensitivity and responsiveness
- • Scratch, liquid, and contaminant resistance due to modern protective layers like tempered glass
- • InnoAioT’s optional optical bonding fills air gaps, enhancing durability, clarity, and vibrancy under bright conditions
However, PCAP touchscreens also have a few downsides:
- • They are prone to unintentional touches
- • They only work with conductive objects, like fingers or special styluses
- • They tend to be more expensive than resistive screens
What is a Resistive Touchscreen?
A resistive touchscreen operates by detecting pressure applied to its surface. It is made up of two flexible layers coated with conductive materials, separated by small gaps or dots. When pressure is applied, the two layers make contact, registering the touch and determining the point of contact.
Resistive touchscreen technology involves a protective top film (usually polycarbonate), followed by a transparent electrode film made of ITO, a spacer layer, and another electrode film. When pressure is applied, the top and bottom films come into contact, causing a voltage change that is registered as a touch input.
Popular Resistive Touch Technologies for Industrial Use
There are two primary types of resistive touch technologies: analog 4-wire and analog 5-wire.
- • 4-wire resistive touchscreens use both electrode films to determine the touch location. They are cost-effective and suitable for simpler applications.
- • 5-wire resistive touchscreens are commonly used in industrial settings because of their durability and reliability. These screens only use the bottom electrode layer, allowing the top film to endure long-term abrasion without affecting performance. The result is increased sensitivity, meaning less pressure is needed to register a touch, and accidental inputs are minimized.
Resistive Touch Features
Although PCAP dominates the touchscreen market, resistive touch technology remains highly relevant in the industrial sector. This is due to its ability to register pressure from any object, including fingers, gloves, and styluses, making it versatile for various applications. Key features of resistive touchscreens include:
- • Low-cost design
- • High power efficiency
- • Resistance to liquids and contaminants
- • The ability to register input from any object, including gloves and styluses
- • Rapid response time
However, resistive touchscreens do have some drawbacks:
- • Image quality is compromised due to multiple layers
- • Protective film degrades over time
- • May require periodic recalibration due to analog drift
- • Not ideal for large screen sizes
Advantages and Disadvantages of Resistive and Projected Capacitive Touchscreens
Resistive Touchscreen
Advantages:
- • Cost-effective
- • Works with any object, including gloves or styluses
- • Durable and resistant to water and dust
Disadvantages:
- • Lower screen clarity due to extra layers
- • Requires physical pressure to register input
- • Limited multi-touch functionality
- • Prone to wear from frequent use
Projected Capacitive
Advantages:
- • Supports multi-touch (e.g., pinch-to-zoom)
- • High sensitivity and accuracy
- • Suitable for finger touch and thin gloves
- • Excellent clarity and durability
Disadvantages:
- • More expensive and complex to manufacture
- • Can be affected by extreme electromagnetic interference
- • Cannot use standard styluses (requires a capacitive stylus)
How to Choose the Right Touch Technology?
Choosing between PCAP and Resistive touch technology depends on factors such as the application environment, user interaction needs, budget, and performance requirements. Here's a quick guide to help you decide:
When to Choose PCAP:
- • Multi-touch: If your application requires multi-touch gestures (e.g., pinch-to-zoom), PCAP is the better choice.
- • User Experience: For high-quality user experience in consumer electronics or interactive kiosks, PCAP offers better responsiveness and sensitivity.
- • Clarity: For applications that need superior visual quality, PCAP offers better clarity due to its single-layer construction.
- • Operating Environment: PCAP is ideal for controlled environments where there are fewer harsh conditions, and the device will be used with bare fingers or thin gloves.
When to Choose Resistive:
- • Cost: Resistive touchscreens are more affordable, making them a great option for budget-conscious projects.
- • Harsh Conditions: In environments where the device will face tough conditions such as outdoor use or exposure to water and dust, resistive touchscreens are a more durable choice.
- • Versatility: If the device needs to work with various input methods (e.g., styluses, gloves, or objects), resistive touchscreens are a better fit.
Future Trends in Touchscreen Technology
As touchscreen technology evolves, PCAP is likely to see enhancements like the integration with flexible displays, better durability, and improved accuracy, expanding into markets such as automotive and healthcare.
Meanwhile, resistive touchscreens may introduce multi-touch features and undergo material upgrades to enhance their longevity and responsiveness. Both technologies are set to improve, becoming more versatile and eco-friendly while meeting the demands of diverse industries.
Why PCAP and Resistive Touch Technologies Matter in Industry
Both PCAP and Resistive touch technologies have revolutionized the industrial sector by providing efficient, durable, and adaptable control interfaces. These technologies reduce the reliance on mechanical buttons and switches, improving the lifespan of devices and simplifying machine design. Touchscreen interaction speeds up operations, making these technologies vital in the growth of industrial automation and control systems.
Tailoring to Every Need: InnoAioT Panel PC Solutions
At InnoAioT, we recognize that each industry has unique demands. That's why our Panel PCs are designed to support both Projected Capacitive (PCAP) and Resistive touch technologies. This flexibility allows us to meet the specific needs of our customers, no matter the operating environment or user interaction requirements. Contact us for more information on our Panel PC solutions.
