P-Core vs E-Core: Understanding the Key Differences in Intel CPUs
Intel has significantly improved its CPU architecture over the past few years. One of the most notable innovations is the introduction of two types of cores in its processors: Performance cores (P-cores) and Efficiency cores (E-cores). This design, called Hybrid Architecture, is part of Intel’s 12th Gen and newer processors. But what are these cores, and why should you care about them? In this article, we’ll break down the differences between P-cores and E-cores, explaining how each one works and what they mean for users.
Keep reading to explore:
- 1. What are P-Cores and E-Cores?
- 2. How Hybrid Architecture Works
- 3. Performance and Power Efficiency
- 4. Applications and Use Cases
- 5. Choosing the Right Processor
What are P-Cores and E-Cores?
● P-Cores: High Performance for Demanding Tasks
P-cores, or Performance cores, are designed to handle heavy tasks. They are optimized for applications that require high computing power, such as gaming, video editing, and running complex simulations. These cores are powerful and capable of running at higher clock speeds, which allows them to tackle intensive workloads.
P-cores also come with Intel’s Hyper-Threading Technology. This enables each P-core to run two threads simultaneously, improving performance for tasks that can benefit from multiple threads.
● E-Cores: Efficiency Without Sacrificing Performance
E-cores, or Efficiency cores, focus on power efficiency. They are designed to handle lighter, less demanding tasks, like browsing the web, streaming media, or running background applications. E-cores operate at lower clock speeds compared to P-cores, but they are highly efficient at processing smaller workloads.
The primary advantage of E-cores is that they help reduce overall power consumption. By shifting less demanding tasks to the E-cores, Intel CPUs can save power and extend battery life in portable devices without sacrificing performance for the user.
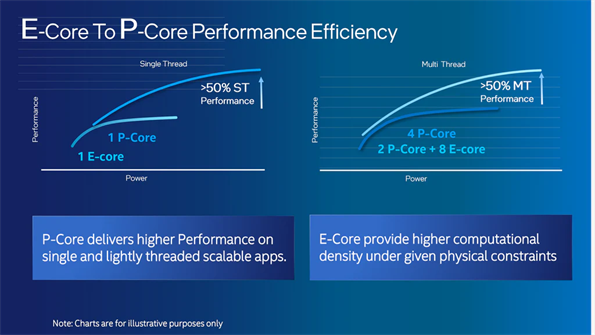
Source: Intel
How Hybrid Architecture Works
Combining the Strengths of P-Cores and E-Cores
Intel’s Hybrid Architecture combines both P-cores and E-cores in the same processor. The goal is to balance performance and power efficiency by assigning tasks to the most appropriate core.
When you run demanding applications, the P-cores take over. These cores will work at full speed to handle tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, or running games. Meanwhile, when the system is idle or running less demanding applications, the E-cores step in to save energy.
This combination allows the CPU to deliver high performance when needed while optimizing power usage for day-to-day tasks. This hybrid approach is particularly beneficial for laptops, where battery life is a concern, but also for desktops where energy consumption can be optimized.
Dynamic Task Scheduling
Intel uses a technology called Thread Director, which intelligently manages how tasks are assigned to the P-cores and E-cores. Thread Director works by monitoring the type of workload and directing lighter tasks to the E-cores and more demanding ones to the P-cores. This dynamic scheduling ensures that the processor operates as efficiently as possible while still maintaining high performance.
Performance and Power Efficiency
● Performance Gains with P-Cores
The primary benefit of P-cores is their ability to handle high-performance tasks. With their higher clock speeds and larger caches, P-cores can process complex tasks much faster than E-cores. This is especially true in single-threaded applications that require a lot of computational power, such as gaming or software development.
P-cores are also essential for multi-threaded tasks, where each P-core can handle multiple threads simultaneously. This is critical for workloads like video rendering or running virtual machines, where processing power is crucial.
● Power Efficiency with E-Cores
E-cores, on the other hand, provide power efficiency without sacrificing too much performance. When the system is running light workloads, the E-cores take over, drawing significantly less power than the P-cores. This results in longer battery life for laptops and less heat generation, making systems quieter and more efficient overall.
While E-cores may not offer the same level of performance as P-cores, they are still capable of running basic applications smoothly. By offloading less demanding tasks to E-cores, users can enjoy a more balanced system that optimizes power consumption without losing too much processing capability.
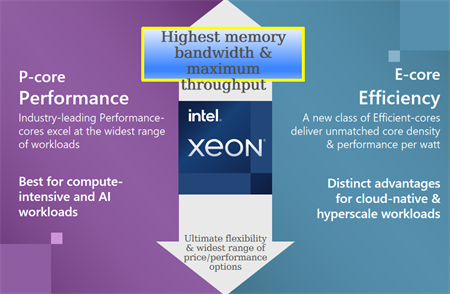
Applications and Use Cases
● Gaming and Content Creation: Where P-Cores Shine
For power users, especially gamers or content creators, the P-cores provide the performance necessary to handle resource-intensive applications. Tasks like gaming, 3D rendering, or video editing benefit greatly from the higher clock speeds and processing power of P-cores. With P-cores taking on these tasks, users can expect smoother experiences and faster performance.
● Everyday Tasks: The Role of E-Cores
For everyday tasks like web browsing, email, and media streaming, the E-cores take over. These tasks don’t require the full power of the P-cores, so E-cores efficiently handle them while conserving energy. As a result, users get a system that feels responsive while being energy-efficient.
E-cores also come into play during multitasking. If you're running multiple background apps or processes, the E-cores can manage those tasks, leaving the P-cores free to handle more demanding applications.
● Portable Devices and Battery Life
One of the biggest benefits of the Hybrid Architecture for portable devices is battery life. Laptops equipped with both P-cores and E-cores can perform demanding tasks using the P-cores while conserving energy with the E-cores when performing lighter workloads. This results in extended battery life without compromising performance during more intense tasks.

Choosing the Right Processor
Why Hybrid Architecture Matters
Intel’s P-core and E-core hybrid architecture is an innovative solution that balances high performance and power efficiency. By combining powerful P-cores with efficient E-cores, Intel processors can optimize energy consumption without sacrificing performance, making them ideal for a wide range of users, from gamers to everyday users to professionals.
Whether you’re looking for raw performance or extended battery life, processors with P-cores and E-cores offer the best of both worlds. By intelligently assigning tasks to the most appropriate cores, Intel ensures your system runs smoothly, efficiently, and at its best.
Final Thoughts
When choosing a CPU, understanding the differences between P-cores and E-cores can help you make an informed decision. If you need a processor that can handle heavy tasks like gaming or video editing, look for CPUs with more powerful P-cores. For users who value power efficiency and long battery life, E-cores will play a key role in ensuring a smooth experience. And with Intel’s Hybrid Architecture, you don’t have to choose between the two—you can have both.
